Hi All,
I have moved my blog to Wordpress in the hopes of receiving more traffic and options for customizing the look and feel. Please visit my blog at https://ambermayse.wordpress.com.
Instructional Integrity - eLearning, Training, Technology, and Leadership
Thursday, October 12, 2017
Monday, December 7, 2015
Seven Tricks to Higher Instructional Designer Salaries
- Make yourself diverse and marketable. Create a professional blog and portfolio to showcase your work and knowledge. Make sure you have a LinkedIn profile and add the links to your blog/portfolio. Post frequently on your blog!
- Increase your knowledge in software, web apps, learning platforms, learning theories and models, and programming languages. Update your resume so you can get the job you truly deserve. Add your LinkedIn URL to your resume.

- Take a position as an hourly contractor instead of a salary employee. Generally speaking, you can make more money as a contractor. Of course it has it draw backs but it's hard to resist a $23k per year increase in pay even if you have to get your own healthcare because there are many affordable plans available. Plus, many contracts can be 1 year or longer and can have extensions. You can even get hired full-time from the company, eventually. Cons are no paid holidays, vacation time or sick time. Pros are pays a lot more, can start soon or quicker than a salaried position, and can turn into a salaried position.
- Move into a specialized area such as corporate training, medical device training, or technical training. In my experience, the field of education did not pay as well for an Instructional Designer. Now, I develop technical training in Articulate Storyline 2 and it pays a lot better. I also find developing technical training more interesting, less political (no deans, chairs, or provosts to contend with), and overall more enjoyable.
- Take on part-time additional contract work. At one point I had a full-time job in addition to a part-time contract position. It was hard to keep up with both but I enjoyed the extra income while it lasted. The part-time position paid $50 per hour!
Here are some links to contract work:- Indeed: http://www.indeed.com/q-Contract-Instructional-Designer-jobs.html
- Remote Instructional Designer Positions on LinkedIn: http://www.indeed.com/q-Remote-Instructional-Designer-jobs.html
- Remote Instructional Designer jobs on Glassdoor: https://www.glassdoor.com/Job/remote-instructional-designer-jobs-SRCH_KO0,29.htm
- Simply Hired: http://www.simplyhired.com/k-contract-instructional-designer-jobs.html
- Teach for an online college part-time in addition to your full-time job. Many community college, small colleges, or online colleges need qualified reliable instructors. If you have a master's degree, you can teach at the Bachelor's level. If you have a doctorate degree, you can teach at the master's and doctoral level. When I taught, I made $3000 per semester. the first semester can be challenging but make sure to copy all your responses and grading comments and you can modify and reuse them each term.
- Write and teach your own courses for a teaching site such as Udemy or Teachable. This can be hard to find the time to do in addition to your full-time job, but once it's created it can be fairly easy to maintain and profit from.
Here is a link to 15 Platforms you can publish and sell your own courses on from Jeff Cobb: http://www.learningrevolution.net/sell-online-courses/
Thursday, November 26, 2015
Instructional Design Strategies
Instructional design
strategies can be combined and applied to design training or courses. I typically combine 4-5 strategies together and apply them in my designs. The reasons for choosing your strategies depends on your audience, content, and purpose.

Retrieved from: https://lsuagcenterode.wordpress.com/2011/08/16/incorporating-learning-styles-into-program-design/

The final product was an Articulate Storyline 2 e-learning course, composed of 50 or more short tutorials that were task-based, included a Title, image, supporting/call out text, and audio with each slide displaying a uniform format. This created ease of learning to the audience.
For the last e-learning tutorials I developed, I included the following strategies:
- Gagne’s 9 Events of Instruction - incorporating this model requires adding details such as a list of topics the learned, introductory video or image and welcoming voice-over. Stimulation of prior knowledge is covered with task-based learning. The screencasts will guide the learner through each task. A survey will be provided at the end to collect feedback.
 Image from UNT Health Science Center
Image from UNT Health Science Center - Cognitive Load Theory – create short screencasts of complicated functions to simplify them. Base each topic on tasks the learner would complete on the job (task-based).

Image from SHIFT's eLearning Blog:
http://info.shiftelearning.com/blog/design-elearning-to-protect-the-learner-from-overload - Incorporating Learning Styles — the Storyline 2 screencasts will provide visual and auditory content in combination with tasked-based learning for problem solving techniques, and concrete facts.

Retrieved from: https://lsuagcenterode.wordpress.com/2011/08/16/incorporating-learning-styles-into-program-design/
- Utilizing Technology – the screencasts will utilize the latest version of Articulate Storyline and will include highlights and zooms. The latest audio technology will also be used to create high quality voice-over.
- Implement Elements and Principles of Design - design each scene with the elements and principles of design to create ease of learning:
- Balance - balance the visual weight of objects, text, color, and space.
- Emphasis - emphasis important text, create a visual hierarchy.
- Movement - this is the path the viewers eye will take
- Pattern- repetition of an object or placement of items.
- Repetition - works with the pattern and creates unity. Repetition of objects and text in scenes creates ease of learning.
- Proportion - the unity created when parts relate with each other.
- Rhythm - one or more elements are used repeatedly, creating the feeling of organization.
- Variety - the use of many elements to hold viewer's attention.
- Unity - harmony between all parts of work.
From: https://www.getty.edu/education/teachers/building_lessons/principles_design.pdf

The final product was an Articulate Storyline 2 e-learning course, composed of 50 or more short tutorials that were task-based, included a Title, image, supporting/call out text, and audio with each slide displaying a uniform format. This created ease of learning to the audience.
Wednesday, November 18, 2015
Templates, Templates, Templates!!!
As an Instructional Designer, templates are EVERYTHING! They help define processes, create consistency, and make designing education and training more efficient and effectively. Templates can be created and used for all aspects of our job from documentation to course or training design in software or an LMS.
Documentation Templates:
Documentation can be created for course and training design to assist with design planning. When I designed courses in higher education, we used templates for designing all aspects of the course. There were documentation templates for the overall design of the course (design document), for the syllabus and for each week of the course.
Here is a generic week 1 overview document:
In designing training, both the analysis and design pieces are both documentation. I use a template for each document.They are both word documents. The analysis document includes the purpose of the document, an overview of the project, the audience or users, implementation, instructional design strategies, an outline of the training, and places for the stakeholders to sign off. The design document includes much of the same information but also includes a project organization and schedule, and details of what will be included in the training.
A script template is also used to streamline the editing and voice-over process.
I've also created templates within the LMS to give courses the same look and feel, and also to make rapid course creation possible.
We also use a template for the software that we use to create the training (currently Articulate Storyline 2).
I love templates!!!
Documentation Templates:
Documentation can be created for course and training design to assist with design planning. When I designed courses in higher education, we used templates for designing all aspects of the course. There were documentation templates for the overall design of the course (design document), for the syllabus and for each week of the course.
Here is a generic week 1 overview document:
A script template is also used to streamline the editing and voice-over process.
I've also created templates within the LMS to give courses the same look and feel, and also to make rapid course creation possible.
We also use a template for the software that we use to create the training (currently Articulate Storyline 2).
I love templates!!!
Friday, November 13, 2015
Using the ADDIE Model to Complete a Training Project
The ADDIE model is the model many companies use to complete a training project. It is an iterative model for continuous improvement as well as a model for initial development.
By Fav203 (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AADDIE_Model_of_Design.jpg
How the ADDIE model can be used to develop training:
By Fav203 (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AADDIE_Model_of_Design.jpg
How the ADDIE model can be used to develop training:
- Analyze - Create a document analyzing the user and their needs. Include: Who is your audience (age, profession, role or title)? What are their needs? What types of tasks will they use the training for? Design the training from the end-users perspective so it's the most applicable to their work flow. Create an outline of what will be included. Who are the stakeholders in this project. Will they need to sign off on this document?
- Design - Create a document detailing out all aspects of the design. This document becomes a living document and can be updated throughout the project. Include a schedule of when you will complete each deliverable in the process. Detail out the outline you created for the analysis and add screen shots of the software if possible. What software or tools will you use to create the training? How will it be implemented (published)? Will the stakeholders need to sign off on this document.
- Develop - This is the development of the actual project. Create the project using the software and tools of your choice. Develop a script for the audio. Script writing can be very difficult. Keep in mind it should speak in an active voice, in present tense and to the user. Ex. To take a screen capture, press the PrtSc button on your keyboard, then click and drag the picture box to the size of your choice. Release the mouse and SnagIt will automatically open with your screen capture.
- Implement - This process should be outlined in your design document. Will you need to publish it to a server? What are the file types that are needed? Will you need to send anyone the link to update a site page? Where will it be archived for the company?
- Evaluate - How will the users evaluate the training so you know it's effective or needs to be improved? For Ex: Was the player easy to use? Did they find the training helpful? Were there topics that should have been included but were not?
Friday, January 2, 2015
Best Practices in eLearning/Hybrid Courses
Beginning an Online Course
From the very beginning, it should be clear how to begin the course. This should included on the Home page with a Start Here button or an indication of "Steps for Getting Started."There should be a list of items students need to complete to get started including reading the syllabus, reviewing the course schedule, exploring the navigation and resources, introducing themselves, etc. For many courses this is included on a Start Here page in a list under the heading "Steps for Getting Started.
For course taught online only, it is also recommended that instructors welcome their students to the class. This can be done through announcements and emails.
Home Page
- Course Code and Title
- Faculty Contact Information
- Course Structure - describes how many weeks or modules, the types of activities, and the methods for learning.
- Link to the Syllabus
- Link to How to Get Started/Start Here
- Technical Support
- Link to the Policies
The Syllabus should include the institution's policies, grading policy, student expectations, and course specific information.
- Course Code and Title
- Course Description- review the your school's course catalog
- Learning Outcomes
- Required materials and textbooks
- Course Schedule
- Prerequisites
- Grading Policy
- Academic Calendar
Module Zero: Getting Started
This module should be before any of the course materials in every course,
- Minimum Technical Requirements
- Technical Support
- Netiquette
- Student Responsibilities
- Plagiarism and Copyright Information
- Policies and Procedures
- Ask the Instructor
- Center for Students with Disabilities (easy access to accommodations)
- Introduce Yourself
- Library
- Academic Support
- Student Support
- Learning Management System Orientation
Measurable Learning Outcomes
Bloom's TaxonomyThere are 3 domains of learning:
- Cognitive: mental skills
- Affective: growth in feelings or emotional areas
- Psychomotor: manual or physical skills
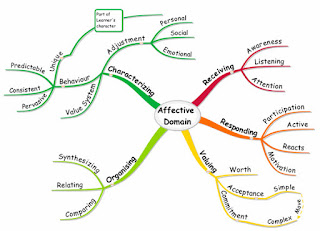
Affective Domain or Emotive or Emotional Skills
Affective Domain Mind Map
Psychomotor Domain or Kinesthetic or Pschyo Motor Skills
Bloom's Taxonomy is great for developing course materials, providing examples of measurable outcomes, and how to align objectives with methods for learning and assessments. Beginning an outcome with a measurable verb will ensure that students complete an action to achieve the learning. Measurable outcomes or objectives could be written using the verbs from the domain images.
Examples of measurable verbs:
- Define how technology can be effectively incorporated into the classroom.
- Discuss specific review standard 2.1 of Quality Matters.
- Demonstrate how to write measurable outcomes in this week's assignment.
- Experiment with the effective design strategies in your own online course.
- Evaluate the three domains of Bloom's Taxonomy in 2-3 paragraphs for this week's discussion.
- Create a video of your thoughts on the three domains of Bloom's Taxonomy and why cognitive domain is mostly used in education.
The Quality Matters Alignment Component
In this presentation we will discuss the alignment component from Quality Matters and writing measurable outcomes/objectives from the three domains of Bloom's Taxonomy.
The program level outcomes should align with the course level outcomes. They should be appropriate for the level of the course. It should be clear how students should meet those objectives. This can be achieved by listing the outcome on the Overview pages and also within the items themselves. This will make it very clear as to what outcomes are met by completing the activity.
According to the Quality Matters Rubric Workbook for Higher Education, alignment is the concept that important course components work together to achieve the intended learning objectives. (2011, p. 7)
There are 6 specific review standards where course materials should align:
- Standard 2.1 "The course learning objectives describe outcomes that are measurable."(2011, p. 6)
- Standard 2.2 "The module/unit learning objectives describe outcomes that are measurable and consistent with the course-level objectives."(2011, p. 6)
- Standard 3.1 "The types of assessments selected measure the stated learning objectives and are consistent with course activities and resources."(2011, p. 8)
- Standard 4.1 "The instructional materials contribute to the achievement of the stated course and module/unit learning objectives."(2011, p. 10)
- Standard 5.1 "The learning activities promote the achievement of the stated learning objectives."( 2011, p. 12)
- Standard 6.1 "The tools and media support the course learning objectives."(2011, p. 14)
As a best practice, review the course description of your course and write your course outcomes to incorporate everything listed in the course description. It would also be a good idea to consult your outcomes with your Chair or Dean before proceeding with the design of your course. Next, decide which outcomes you want to be covered in each week or module of your course. Using this process ensures all materials are developed around the course outcomes.
Reference
Affective Domain Mind Map [image]. Retrieved July 31, 2014 fromhttp://www.biggerplate.com/mapImages/xl/72f4a928-8d88-4aa2-85da-8fa21ba5cf30.png(Links to an external site.)
Atkinson, S. (2011)Taxonomy of Educational Objectives Psychomotor Domain [image]. Retrieved July 31, 2014 fromhttp://spatkinson.wordpress.com/2012/10/17/visualising-outcomes-domains-taxonomies-and-verbs/(Links to an external site.)
PCSelemliteracy (2012)Bloom's Taxonomy Revised [image]. Retrieved July 31, 2014 fromhttp://pcs2ndgrade.pbworks.com/f/1318607148/RBT.PNG(Links to an external site.)
Quality Matters (n.d.) QM logo [image]. Retrieved July 31, 2014 fromhttp://usfspdistancelearning.files.wordpress.com/2013/05/qm-logo.jpg(Links to an external site.)
Quality matters rubric workbook for higher education(2011-2013 Edition) . (2011) Baltimore, MD: MarylandOnline Inc.
Assessments and Activities
Assessments and activities should align with the course objectives, be engaging, and utilize technology.Assignments should not just be included to be "busy work." They should be meaningful, facilitate learning, and possibly even fun. They should also vary throughout the course to allow students multiple assessment opportunities.According to the Quality Matters Standard 3, "assessments strategies are designed to evaluate student progress by reference to stated learning objectives; to measure the effectiveness of student learning; and to be integral to the learning process."
The learning objective can be referenced within the assignment instructions to ensure student's are aware of the exact objective they are obtaining by completing the assignment.
Types of Assessments and Activities:
- Play educational games.
- Research and write papers.
- Complete polls and surveys.
- Participate in discussions
- Traditional Quizzes and Exams.
- Answer questions in a shelf-check.
- ePortfolios - can use a free app (Weebly/Yola site, or a blog) or one that is built into the eLearning environment.
- Create flash cards - using StudyMate or one of the many apps available:http://www.flashcardapps.info(Links to an external site.)
- Compose drawings, sketches, mind maps, or math equations with a digital white board -http://www.teachthought.com/apps-2/7-apps-to-turn-your-ipad-into-a-digital-whiteboard/(Links to an external site.)
- Develop quiz and test questions - students can create their own quiz and test questions that can then be incorporated into a test bank.
- Create a group or individual presentations using free or inexpensive web applications such as Animoto, Prezi, Screencast-o-matic.
- Design polls and surveys to send to their fellow classmates using SurveyMonkey or other survey apps.
- Write their own discussions for their classmates to answer.
- Create forms and documents either individually or as a group.
- Produce videos and podcasts as a means to complete their assignment. For example, instead of writing a short story and submitting a word document, students could write a short story and record it as a video or as a podcast. Audacity is free audio software.
- Interview someone using audio or video.
- Publish ebooks - students (or anyone for that matter) can publish their own ebook:http://www.myebook.com/index.php?option=take_tour(Links to an external site.)
Example Presentations:
Global Warming Presentation
(GreenandSustainable, 2010) Global Warming. Animoto presentation created by Amber Olson for the University of Colorado.
Reference
Graham, T. (2012)Screen capture of a student portfolio from Clemson University [image].Retrieved July 31, 2014from:http://www.clemson.edu/academics/programs/eportfolio/images/gallery/graham.jpg
Olson, A. (2010)Global Warming [video]. Retrieved July 31, 2014fromhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=01aLyBOnbBg&index=3&list=UUpLCpsOX4eIXn1F4jGhbAZA
Mayse, A. (2014) Benefits of using OERs mindmap [image]. Retreived November 4, 2014 from:http://www.mindmeister.com/457936286/benefits-of-using-open-education-resources-oers
Tomas, L. (2009) Screen capture of a student portfolio from LaGuardia Community College Nursing Program [image].Retrieved July 31, 2014 from: https://s3.amazonaws.com/files.digication.com/M2ae96bfd7ade07a6bccbe4ae533f7184.png
Interaction in Online Learning Environments
Classroom InteractionIn order for interaction to occur in an online environment, students need opportunities to connect to both their fellow classmates and their instructor. These opportunities include group projects, discussion forums, social learning sites, and virtual meeting areas. These items can be designed into the course to encourage interaction and make the learning environment more engaging.
A discussion forum is one of the most common opportunities an online student has to interact with their fellow classmates. It also provides an opportunity for the instructor to become more involved in their learning in addition to providing feedback on assessments. Students can otherwise feel isolated, alone, and not on track. Discussion forums allow for students to feel reassured that they are correct in their thinking and understanding. When the instructor responds to students post in a discussion forum, wiki, blog etc., the instructor can ask additional questions to guide the learning and verify that the student is correct in their assumptions so they feel reassured.
Discussions can also be redundant and boring. To avoid boring and redundant discussions, try requiring the discussion to be a video or audio discussion. Other methods for discussions can be using live chat, social networking, a web app such as Voice Thread, or conference tool.
Web Conferencing
There are many web conferencing software/apps available to have live session with your students.
Google Plus can be used to host a private live session in a Hangout or create a private community for you and your learners to use as a social networking space.
Faculty Feedback
Additional Opportunities for a faculty member or part time instructor to provide feedback to their students includes when grading or reviewing assignments and quizzes or tests. Quizzes or tests need to be designed to provide feedback on if the question is correct or incorrect and information on why the answer is correct or not correct.
Creating an Engaging Learning Environment
Tips for making the learning environment more engaging:- Try to keep the design of the course simple and elegant through the use of instructional design concepts. See Module 9: Structure and Design for additional information.
- Break up text with videos, images, and audio files. To many paragraphs without a visual can overwhelm students. Reinforce the material with instructional images.
- Don't regurgitate a textbook. Assign reading from the textbook and reinforce interesting aspects from the text. You can include a quiz on the text to insure students are reading.
- Design materials around learning outcomes instead of the textbook. What is the most interesting aspects related to the materials?
- How does this material apply to "real life?" Creating this connection will allow students to see the value in the information.
- Do not include death by slideshow presentations (PowerPoint, Slideshow, Prezi).
Watch the following funny video: Life After Death by Powerpoint 2010 by Don McMillan
(McMillan, 2010) - Instead, try creating materials that include emotional connection by using video, images, and stories.
Story, Imagery, and the Art of 21st Century Presentation- Garr Reynolds at TED x Kyoto(TEDx Talks, 2012) - Encompass stories describing personal and professional experiences and analogies. Encourage students to reflect on their experiences and share their stories.
Example Digital Story by Yukkiko Nishimura - Facilitate a community of learning or encourage social learning. There are many apps that can be used for education.
- Include discussions each week where students can connect to each other. Within the discussion, instructors can encourage related ideas and interesting facts.
- Encourage and inspire your students. Help students visualize of the rewards of learning this materials, finishing the course, obtaining the degree, and the doors that will open to them as a result.
- Challenge students with technology and application of knowledge. Present challenges that get your students thinking.
- Provide affirmation to your students. Reward their ideas. Remember to praise in public but discuss negatives in private.
Nishimura, Y. (2013) Adapting to a new cuture. [video] Retrieved November 5, 2014 from: http://digitalstorytelling.coe.uh.edu/view_story.cfm?vid=411&otherid=featured&d_title=Featured%20Digital%20Stories
McMillian, D. (2010, November 9) Life after death by powerpoint 2010. [video] Retrieved November 5, 2014 from: http://youtu.be/KbSPPFYxx3o
TEDxTalks. (2012, October 17) Story, Imagery, & the Art of 21st Century Presentation: Garr Reynolds at TEDxKyoto 2012 [video] Retrieved November 5, 2014 from http://youtu.be/zQpGf1gPY7M
Teaching and Learning with Technology
According to the ISTE Position Statement on The Common Core State Standards: “Technology, used effectively, can help all students meet and exceed the rigorous learning goals embedded in the Common Core State Standards by providing access to tools and resources that personalize instruction and creating rich, engaging and relevant learning environments.”
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ulb4jl3xqs8
Many people use technology in their everyday lives whether its for
social or professional networking, including examples of their work in a
professional blog, reading or researching, checking a bank account, or
playing games for fun. Weaving technology throughout your course will
make it more engaging and fun. According to Schmidt and Hawkins
"Demographers and social researchers have banged on endlessly about gen Y
and their rapid embrace of new technology but gen Z is the first
generation born into a digital world." Generation Y are people born from
1977-1994, while people born between 1995-2012 are considered
Generation Z. (Schroer, n.d., pg. 3) Generation Z students are just
starting college and have used technology their entire lives (digital
natives).Adding More Technology to Online Classrooms
Using multiple methods for delivering educational materials to your students can be an engaging and effective way for your students to digest information. In addition to text, create videos, interactive presentations with voice-over and images (see Module 5 - Presentation: Tips for Creating an Engaging Learning Environment), screen casts on how to use software or complete tasks, include funny images, and digital stories. It could also be a good idea to create an online learning community using free educational applications.
Try to encourage students to use technology as much as possible. You can have students use web apps and media as part of completing assignments, projects, discussions, and group work. Consider incorporating social networking, tweeting, journal blogs, presentations, podcating, videos (students can record videos using their Smart Phones), screencasts, digital storytelling, eBooks, images, and web conferences.Many web apps are free and allow students to create fun, interesting assignments which provides another opportunity for students to measure their own learning (QM Standard 3.5).
New web applications are being developed everyday. It's best to search for current and new web apps.
Technology for Teaching and Learning
The following are free tools unless otherwise specified.
- Audio Recording - Audacity(Links to an external site.)
- Blogs – Edublog(Links to an external site.), WordPress(Links to an external site.), Glogster EDU(Links to an external site.)
- Charts and Graphs - Tableau Public(Links to an external site.), iCharts(Links to an external site.)
- Educational Games - Living Math(Links to an external site.), Lumosity(Links to an external site.), Active Worlds(Links to an external site.), Cyber Ciege(Links to an external site.), EntropiaUniverse(Links to an external site.), Kaneva(Links to an external site.), Cell Craft(Links to an external site.)
- E-Portfolios - Blogs, Weebly(Links to an external site.), Yola(Links to an external site.)
- Digital Storytelling - Audacity(Links to an external site.)(voice story), Screencast-o-matic(Links to an external site.)(upload pictures and videos and record voice-over),
- Infographics -Easel.Ly(Links to an external site.),Piktochart(Links to an external site.),Visualize Me(Links to an external site.)(infographic resume), Venngage(Links to an external site.), Infogr.am(Links to an external site.), Visual.Ly(Links to an external site.)
- Interactive Maps - Charts Bin(Links to an external site.), Stat Silk(Links to an external site.)
- (Links to an external site.)Mind Maps - Mind Meister(Links to an external site.), The Brain(Links to an external site.), Mind Genius(Links to an external site.), Mind Mapping(Links to an external site.)
- Timelines – Dipity(Links to an external site.), Timeline JS(Links to an external site.)
- Organizing -Online Weekly Planner(Links to an external site.),My Study Life(Links to an external site.)
- Presentations – Prezi(Links to an external site.), Screencast-o-matic(Links to an external site.),Camtasia(Links to an external site.) (free trial), Adobe Captivate(Links to an external site.) (free trial), EZVid(Links to an external site.), Articulate(Links to an external site.) (free trial)
- Screencasts - Jing(Links to an external site.), Screencast-o-matic(Links to an external site.), Camtasia(Links to an external site.)(free trial),Adobe Captivate(Links to an external site.)(free trial)
- Social Networks -Edmodo(Links to an external site.),Cel.ly(Links to an external site.),
- Videos - Video tool in Canvas, Smart Phone video camera, Animoto(Links to an external site.),Digital Films(Links to an external site.)
- Video Editing/Production - iMovie (comes with Macs), Windows Movie Maker
- Web Conferencing - Google + Handouts(Links to an external site.), Adobe Connect (Links to an external site.)(free trial), WebX(Links to an external site.), Big Blue Button(Links to an external site.) (free through Canvas - Conferences tab)
- Word Cloud - Wordle(Links to an external site.), Tagxedo(Links to an external site.)
Resources:
- 20+ Tools to Create Your Own Inforgraphics(Links to an external site.)
- (Links to an external site.)Kathy Shrocks Guide to Everything -Digital Storytelling(Links to an external site.)
- 50 Great Sites for Serious Educational Games(Links to an external site.)
References
ISTE (2014).ISTE Position Statement on theCommon Core State Standards. Retrieved December 22, 2014 fromhttp://www.iste.org/standards/common-core
Schmidt, L. and Hawkins, P. (2008 July 15). Children of the tech revolution. The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved December 18, 2014 from http://www.smh.com.au/news/parenting/children-of-the-tech-revolution/2008/07/15/1215887601694.html(Links to an external site.)
Schroer, W. (n.d.). Generations X,Y, Z and the Others. Retrieved December 22, 2014 fromhttp://www.socialmarketing.org/newsletter/features/generation1.htm
Wednesday, April 23, 2014
Quality Matter - Professional Development
I recently took the Quality Matters workshop on "Applying the QM Rubric. This was an online two week long course that is a prerequisite in becoming a Certified QM Reviewer.
One of the main concepts covered in the first module was the difference between design and delivery. Design is the anticipating and planning. The delivery is the actual teaching of the course and faculty performance. QM is about the design.
Along with reading over all the criteria in the QM rubric, I discovered the Universal Guide to Learning (UGL)http://www.udlcenter.org/ and Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) http://www.w3.org/WAI/intro/wcag. These two guides will be helpful in designing course for students with disabilities.
Most of the criteria in the rubric confirms how I already design courses but now I understand how and why these criteria are important. One area that many colleges may lack in student access to resources such as minimal technical requirements, tech support, students with disability information and easy access to accommodations, library resources, and academic support. These are essential and should be present in the beginning of a course.
Outcomes is also another very important aspect of QM. Outcomes should be clear, measurable, written from the student's perspective, indicated where they are met within the course materials, and properly aligned with the level of the activity or assessment. So often, the outcome is measurable and clear but it is not apparent where the outcome is met nor is it level with the type of activity or assessment. For example, the outcome is "Identify principals of design" but the assessment is designing packaging for a product. The is not the appropriate level. The outcome should be revised to "Design a package for a product using the principals of design."
I greatly enjoyed the QM workshop and have been passionate about applying the rubric to design templates, courses, and faculty and staff training. In the future, I hope I can take the certificate program and become a QM trainer or reviewer.
One of the main concepts covered in the first module was the difference between design and delivery. Design is the anticipating and planning. The delivery is the actual teaching of the course and faculty performance. QM is about the design.
Along with reading over all the criteria in the QM rubric, I discovered the Universal Guide to Learning (UGL)http://www.udlcenter.org/ and Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) http://www.w3.org/WAI/intro/wcag. These two guides will be helpful in designing course for students with disabilities.
Most of the criteria in the rubric confirms how I already design courses but now I understand how and why these criteria are important. One area that many colleges may lack in student access to resources such as minimal technical requirements, tech support, students with disability information and easy access to accommodations, library resources, and academic support. These are essential and should be present in the beginning of a course.
Outcomes is also another very important aspect of QM. Outcomes should be clear, measurable, written from the student's perspective, indicated where they are met within the course materials, and properly aligned with the level of the activity or assessment. So often, the outcome is measurable and clear but it is not apparent where the outcome is met nor is it level with the type of activity or assessment. For example, the outcome is "Identify principals of design" but the assessment is designing packaging for a product. The is not the appropriate level. The outcome should be revised to "Design a package for a product using the principals of design."
I greatly enjoyed the QM workshop and have been passionate about applying the rubric to design templates, courses, and faculty and staff training. In the future, I hope I can take the certificate program and become a QM trainer or reviewer.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)